Auxiliary Objects
9 minute read
BibReference Model
The BibReference table contains basically BibTex formatted references stored in the bibtex column. You may easily import references into OpenDataBio by just specifying the doi, or simply uploading a bibtex record. These bibliographic references may be used to:
- Store references for Datasets - with the option of defining references for which citation is mandatory when using the dataset in publications; but all references that have used the dataset may be linked to the dataset; links are done with a Pivot table named
dataset_bibreference; - Store the references for Taxons:
- to specify the reference in which the Taxon name was described, currently mandatory in some Taxonomic journals like PhytoTaxa. This description reference is stored in the
bibreference_idof the Taxons table. - to register any reference to a Taxon name, which are then linked through a pivot table named
taxons_bibreference.
- to specify the reference in which the Taxon name was described, currently mandatory in some Taxonomic journals like PhytoTaxa. This description reference is stored in the
- Link a Measurement to a published source;
- Indicate the source of a Trait definition.
- Indicate mandatory citations for a Dataset, or link references using the data to a Dataset
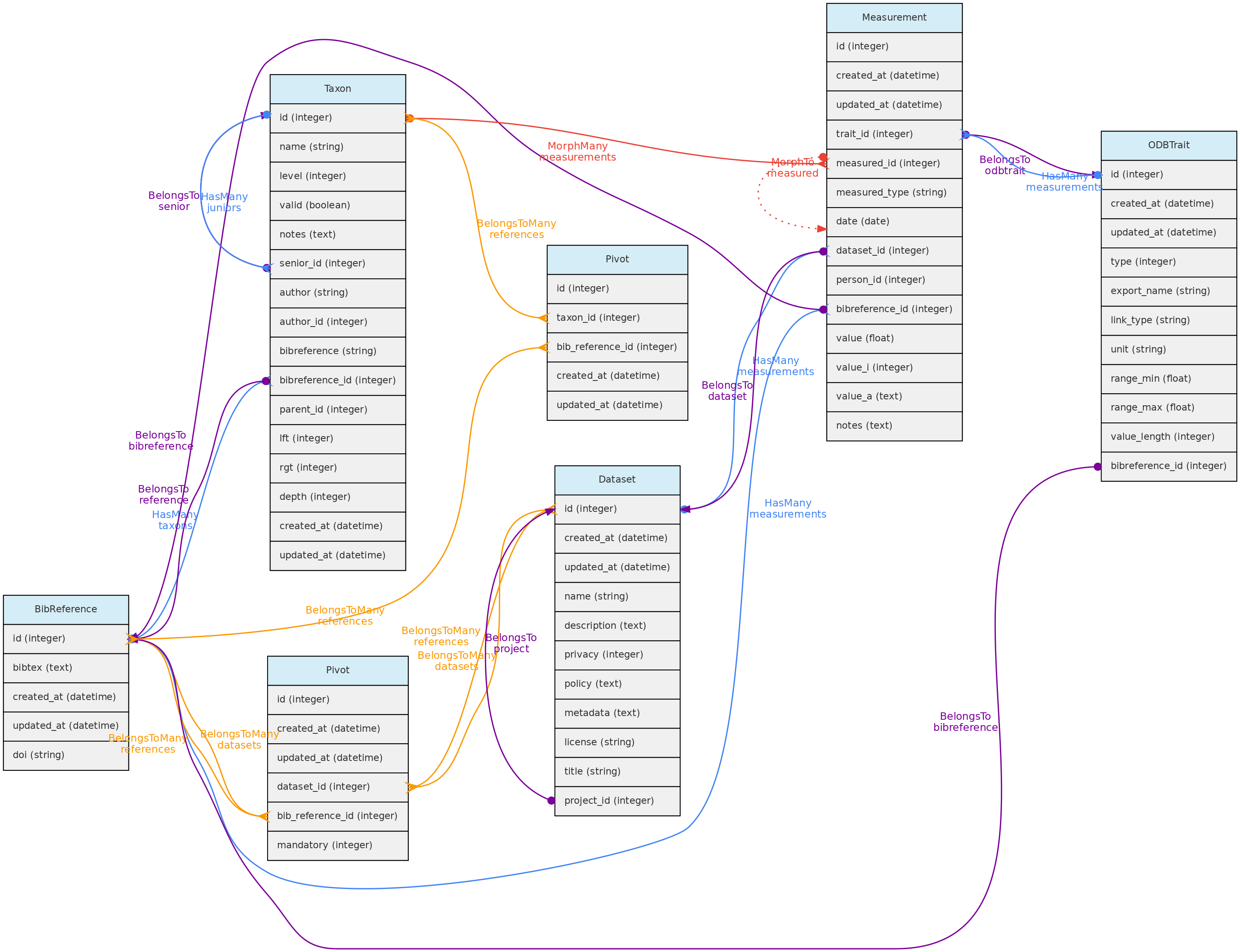 BibReference model and its relationships. Lines linking tables indicate the
BibReference model and its relationships. Lines linking tables indicate the methods implemented, with colors indicating different Eloquent relationships.
Bibreferences table
- The BibtexKey, authors and other relevant fields are extracted from the
bibtexcolumn. - The Bibtexkey must be unique in the database, and a helper function is be provided to standardize it with format
<von? last name> <year> <first word of title>. The “von part” of the name is the “von”, “di”, “de la”, which are part of the last name for some authors. The first word of the title ignores common stop-words such as “a”, “the”, or “in”. - DOIs for a BibReference may be specified either in the relevant BibTex field or in a separate text input, and are stored in the
doifield when present. An external API finds the bibliographic record when a user informs thedoi.
**Data access** [full users](/en/docs/concepts/data-access/#user) may register new references, edit references details and remove reference records that have no associated data. BibReferences have public access!
Identification Model
The Identification table represents the taxonomic identification of Individuals.
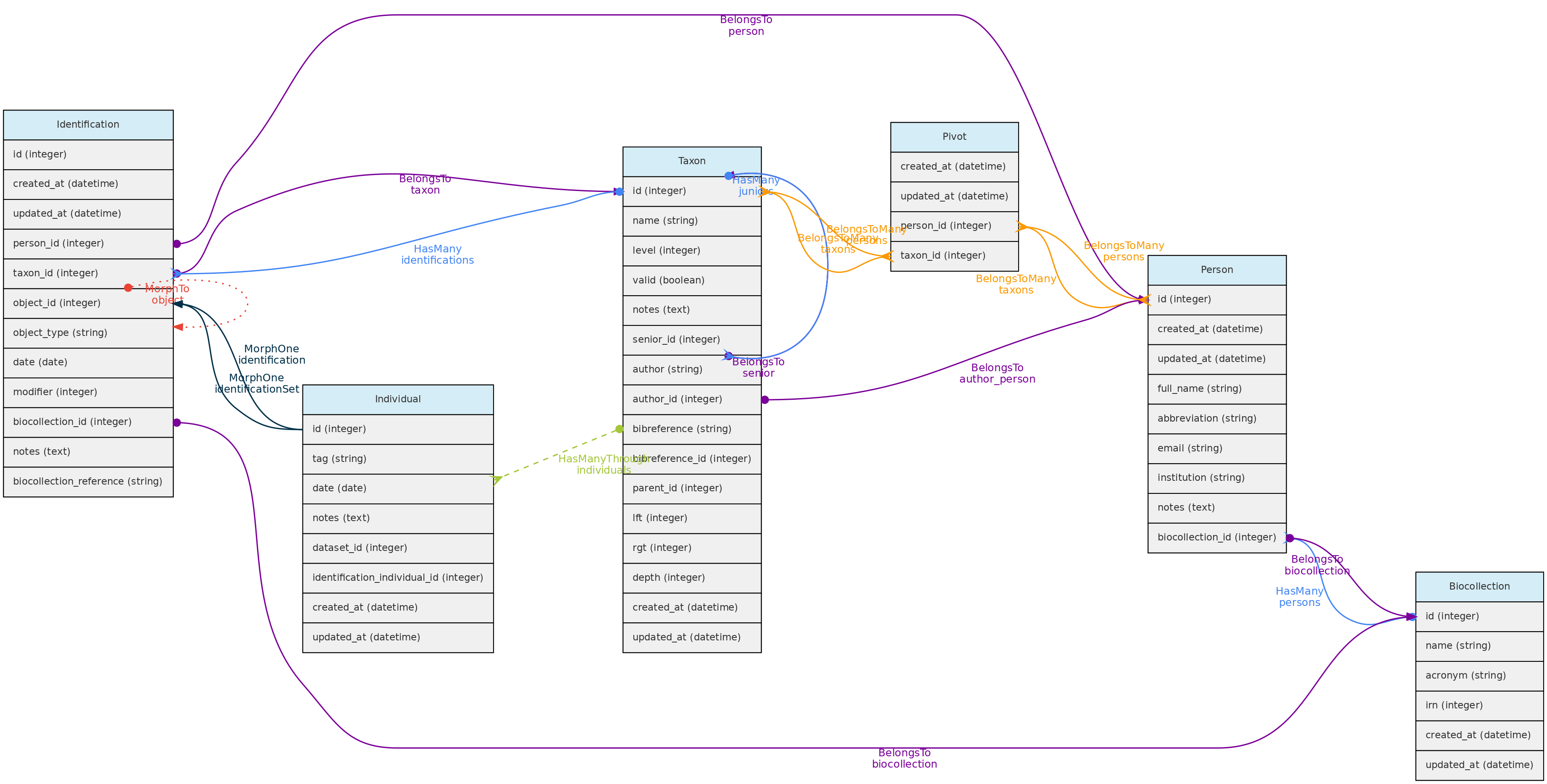 Identification model and its relationships. Lines linking tables indicate the
Identification model and its relationships. Lines linking tables indicate the methods implemented, with colors indicating different Laravel Eloquent relationships
Identifications table
- The Identification model includes several optional fields, but in addition to
taxon_id,person_id, the Person responsible for the identification, and the identificationdateare mandatory.
- The
datevalue may be an Incomplete Date, e.g. only the year or year+month may be recorded.
- The following fields are optional:
modifier- is a numeric code appending a taxonomic modifier to the name. Possible values ’s.s.’=1, ’s.l.’=2, ‘cf.’=3, ‘aff.’=4, ‘vel aff.’=5, defaults to 0 (none).notes- a text of choice, useful for adding comments to the identification.biocollection_idandbiocollection_reference- these fields are to be used to indicate that the identification is based upon comparison to a voucher deposited in a Biological Collection and creates a link between the Individual identified and the BioCollection specimen from which the identification is based upon.biocollection_idstores the Biocollection id, andbiocollection_referencethe unique identifier of the specimen compared, i.e. would be the equivalent of thebiocollection_numberof the Voucher model, but this reference does not need to be from a voucher registered in the database.
- The relationship with the Individual model is defined by a polymorphic relationship using fields
object_typeandobject_id[This could be replaced by an ‘individual_id’ in the identification table. The polymorphic relation inherited from a previous development version, kept because the Identification model may be used in the future to link Identifications to Measurements]. - Changes in identifications are audited for tracking change history
Data access: identifications are attributes of Individuals and do not have independent access!
Person Model
The Person object stores persons names, which may or may not be a User directly involved with the database. It is used to store information about people that are:
* collectors of Vouchers, Individuals and MediaFiles
* taxonomic determinators or identifiers of individuals;
* measurer of Measurements;
* authors for unpublished Taxon names;
* taxonomic specialists - linked with Taxon model by a pivot table named person_taxon;
* dataset authors - defining authors for the dynamic publication of datasets;
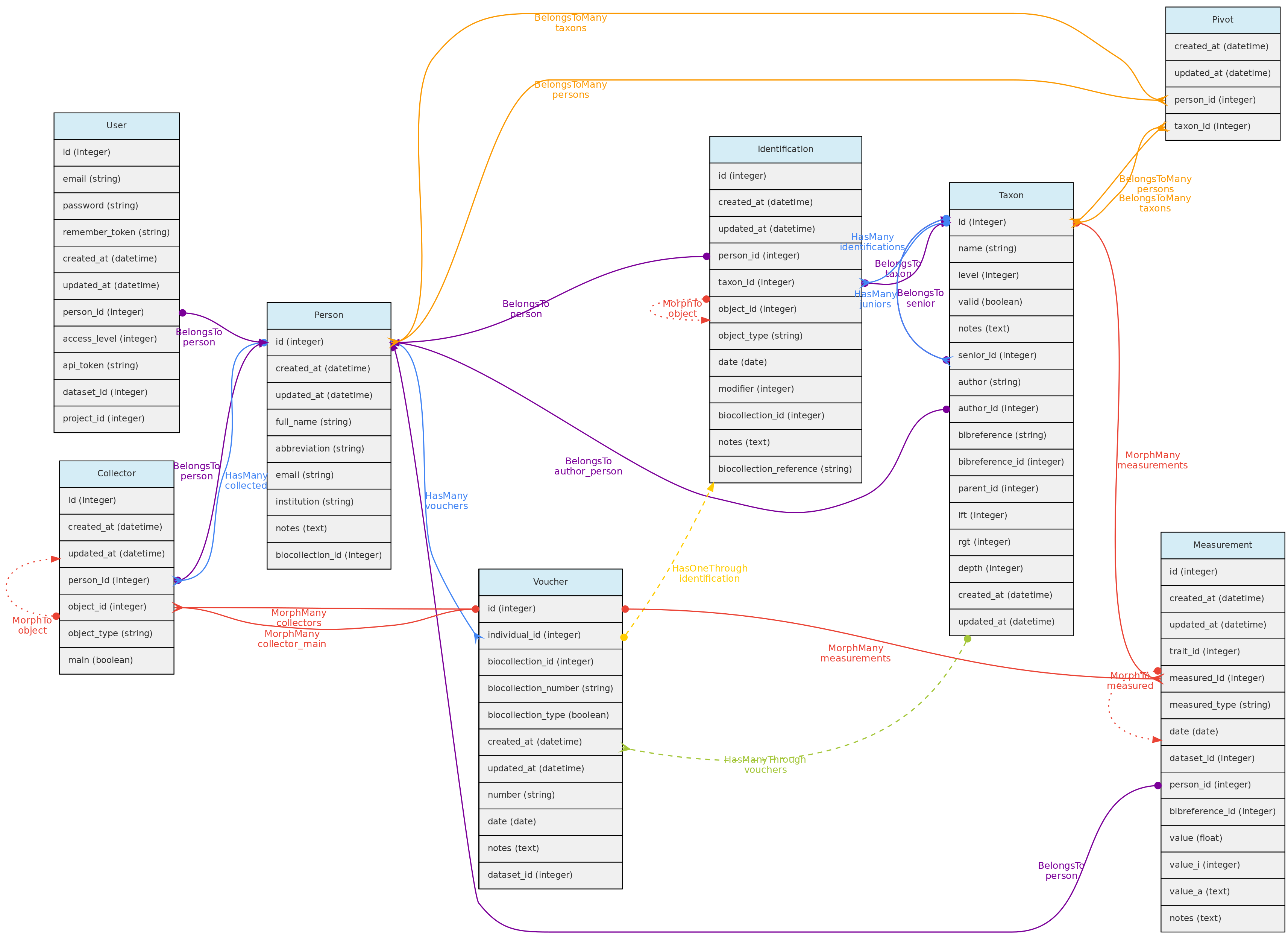 Person model and its relationships. Lines linking tables indicate the
Person model and its relationships. Lines linking tables indicate the methods implemented, with colors indicating different types of Laravel Eloquent methods, solid lines the direct and dashed the indirect relationships
Persons table
- mandatory columns are the person
full_nameandabbreviation; - when registering a new person, the system suggests the name
abbreviation, but the user is free to change it to better adapt it to the usual abbreviation used by each person. The abbreviation must be unique in the database, duplicates are not allowed in the Persons table. Therefore, two persons with the exact same name must be differentiated somehow in theabbreviationcolumn. - The
biocollection_idcolumn of the Persons table is used to list to which Biocollection a person is associated, which may be used when the Person is also a taxonomic specialist. - Additionally, the
emailandinstitutionthe person belongs to may also be informed. - Each user can be linked to a Person by the
person_idin the User table. This person is then used the ‘default’ person when the user is logged into the system.
**Data access** [full users](/en/docs/concepts/data-access/#user) may register new persons and edit the persons they have inserted and remove persons that have no associated data. Admins may edit any Person. Persons list have public access.
Media Model
Media files are similar to measurements in that they might be associated with any core object. Media files may be images (jpeg, png, gif, tif), video or audio files and can be made freely accessible or placed in a Dataset with a defined access policy. A CreativeCommons.org license must be assigned to them. Media files may be tagged, i.e. you may define keywords to them, allowing to query them by Tags. For example, an individual image may be tagged with ‘flowers’ or ‘fruits’ to indicate what is in the image, or a tag that informs about image quality.
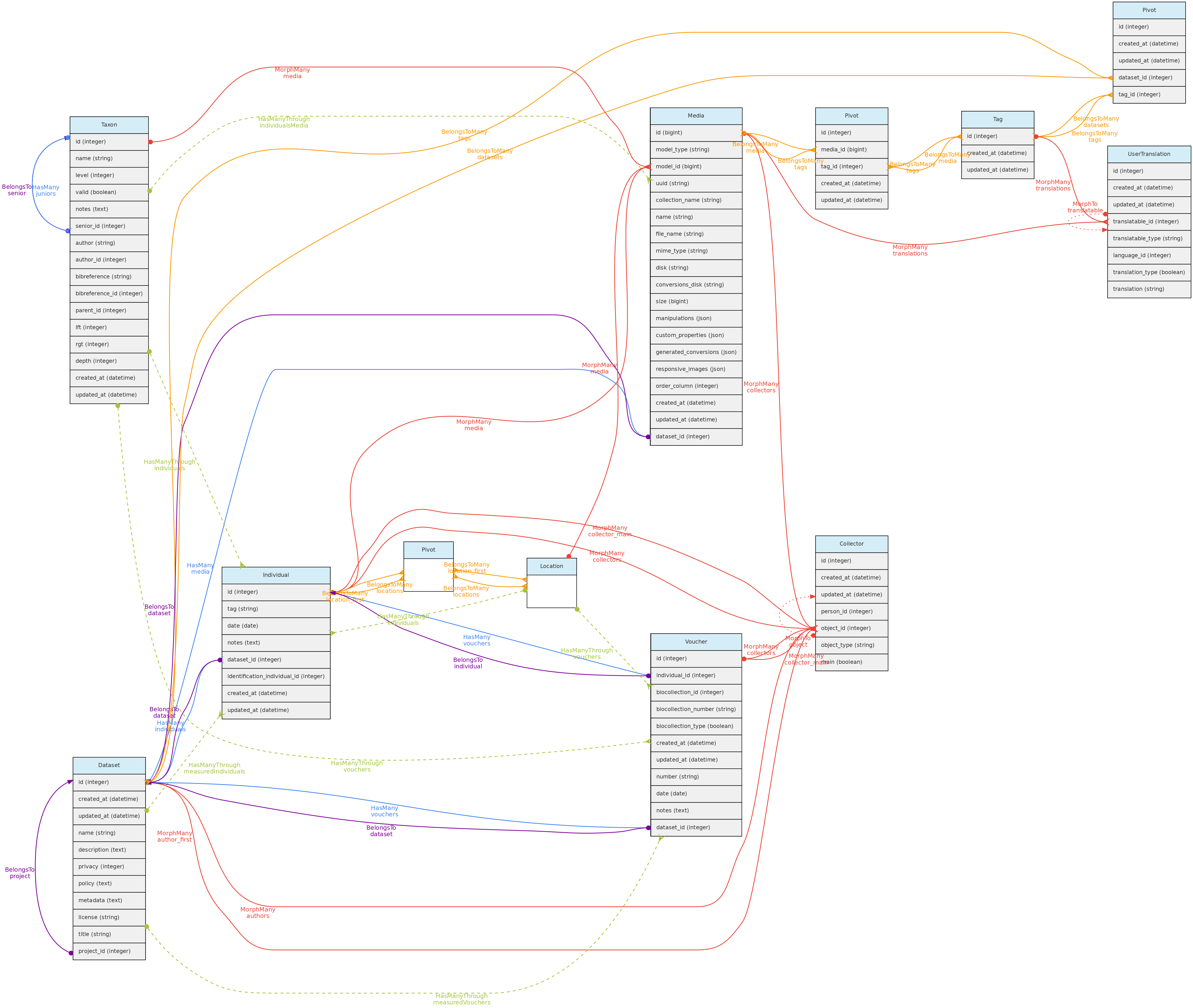
- Media files (image, video, audio) are linked to the Core-Objects through a polymorphic relationship defined by columns
model_idandmodel_type. - Multiple Persons may be associated with the Media for credits, these are linked with the Collectors table and its polymorphic relationship structure.
- A Media may have a
descriptionin each language configured in the Language table, which will be stored in theuser_translationstable, which relates to the Tag model through a polymorphic relationship. Inputs for each language are shown in the web-interface forms. - Media files are not stored in the database, but in the server storage folder.
- It is possible to batch upload media files through the web interface, requiring also a file informing the objects to link the media with.
Data access full users may register media files and delete the ones they have inserted. If Media is in a Dataset, dataset admins may delete the media in addition to the user. Media files have public access, except when linked to a Dataset with access restrictions.
Tag Model
The Tag model allows users to define translatable keywords that may be used to flag Datasets, Projects or MediaFiles. The Tag model is linked with these objects through a pivot table for each, named dataset_tag, project_tag and media_tag, respectively.
A Tag may have name and description in each language configured in the Language table, which will be stored in the user_translations table, which relates to the Tag model through a polymorphic relationship. Inputs for each language are shown in the web-interface forms.
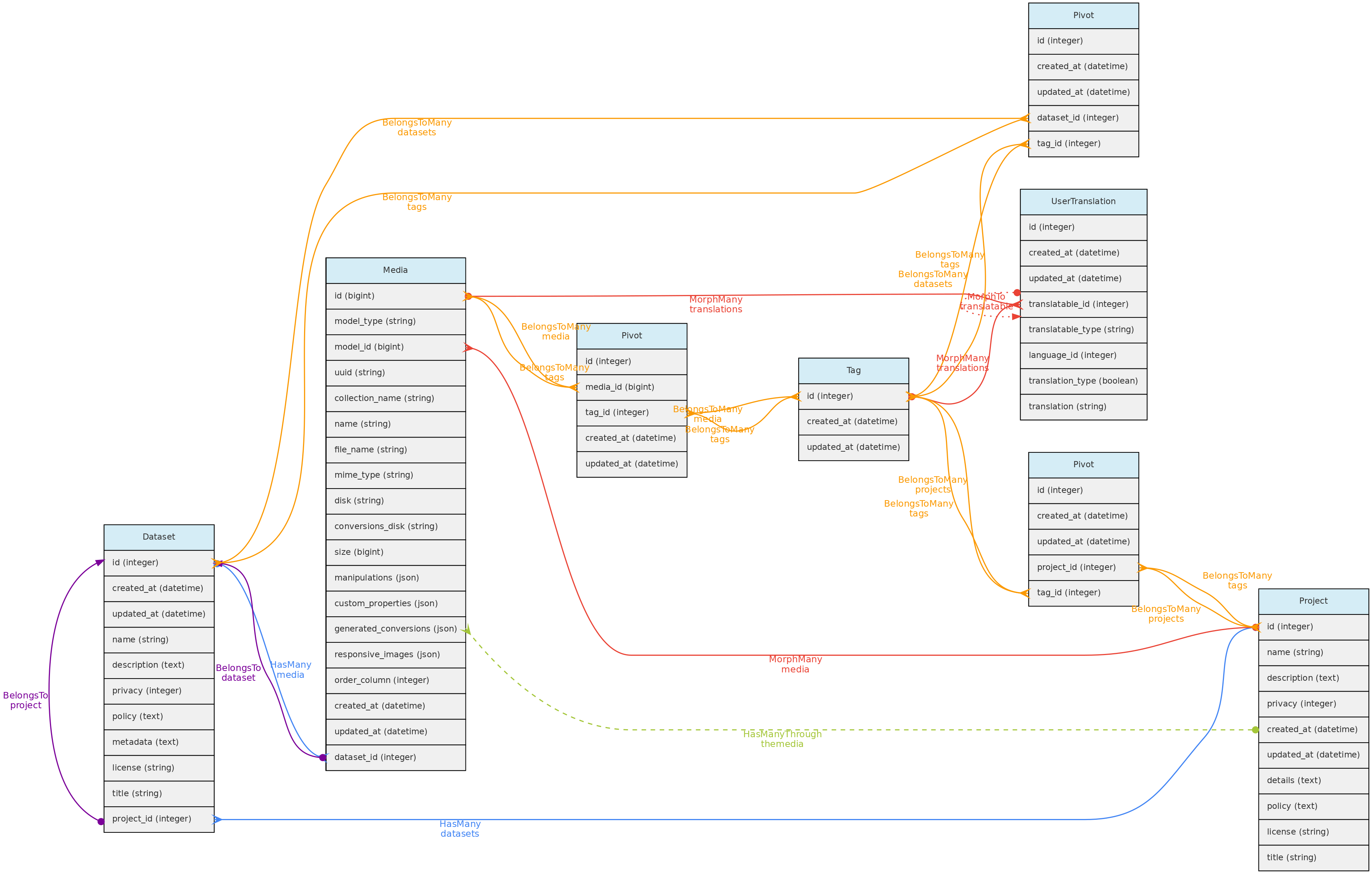
Data access full users may register tags, edit those they have inserted and delete those that have not been used. Tags have public access as they are just keywords to facilitate navigation.
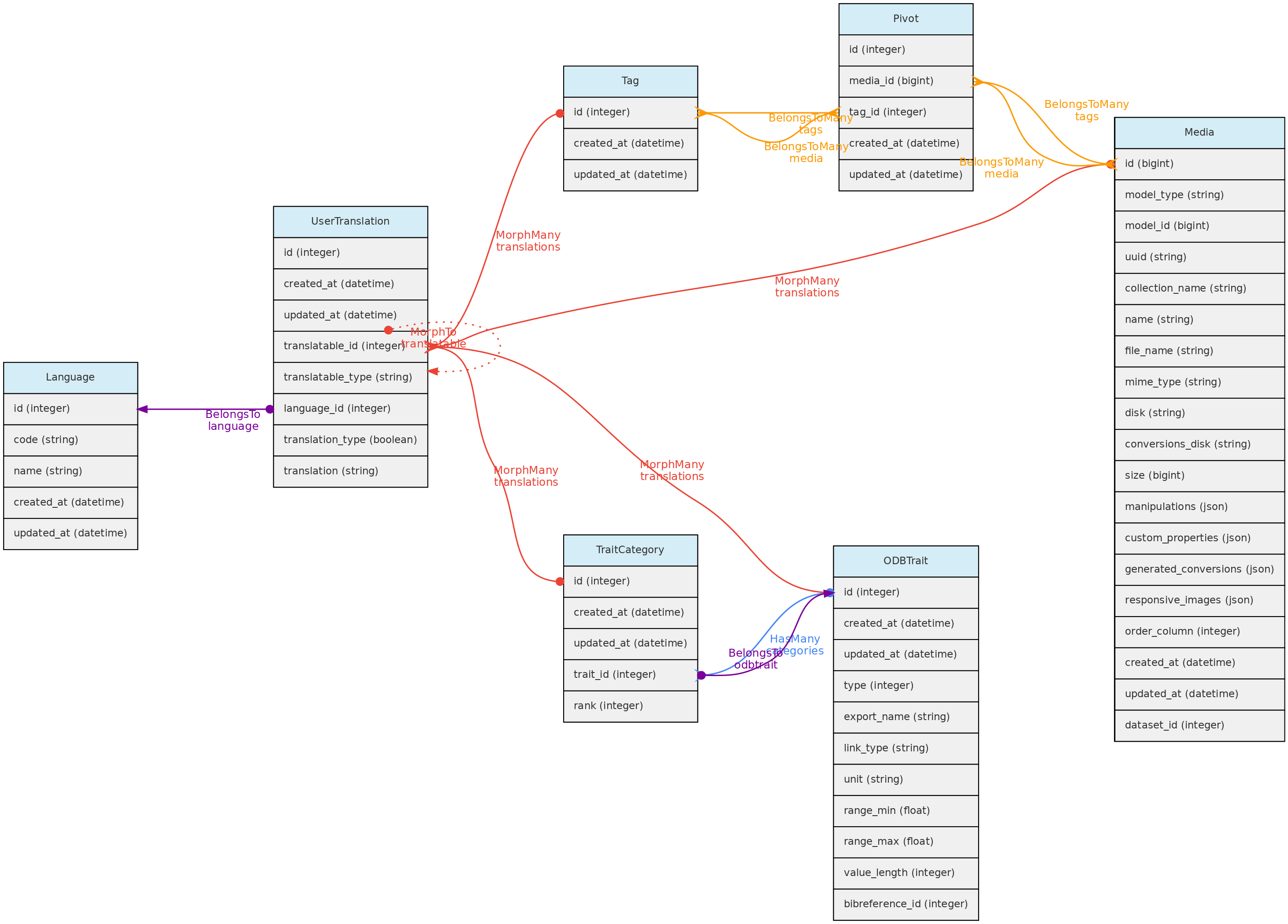
User Translation Model
The UserTranslation model translates user data: Trait and Trait Categories names and descriptions, MediaFiles descriptions and Tags. The relations between these models are established by polymorphic relations using fields translatable_type and translatable_id. This model permits translations to any language listed in the Language table, which is currently only accessible for insertion and edition directly in the SQL database. Input forms in the web interface will be listed for registered Languages.
Vernacular - Popular Name
The Vernacular and VernacularCitation templates allow you to record popular names of organisms by relating them to Taxons and/or Individuals. Names must be unique in the Vernacular table, and each record can be linked to multiple Taxa and/or Individuals, depending on the information sources. Each record can also have one or more citations (citation text + BibReference + note).
Incomplete Dates
Dates for Vouchers, Individuals, Measurements and Identifications may be Incomplete, but at least year is mandatory in all cases. The date columns in the tables are of ‘date’ type, and incomplete dates are stored having 00 in the missing part: ‘2005-00-00’ when only year is known; ‘1988-08-00’ when only month is known.
Auditing
Modifications in database records are logged to the activity_log table. This table is generated by the package ActivityLog. The activities are shown in a ‘History’ link provided in the Show.view of the models.
- The package stores changes as json in the
propertiesfield, which contains two elements:attributesandold, which are basically the new vs old values that have been changed. This structure must be respected. - Class ActivityFunctions contain custom functions to read the the properties Json record stored in the
activity_logtable and finds the values to show in the History datatable; - Most changes are logged by the package as a ’trait’ called within the Class. These allow to automatically log most updates and are all configured to log only the fields that have changed, not entire records (option
dirty). Also record creation are not logged as activity, only changes. - Some changes, like Individual and Vouchers collectors and identifications are manually logged, as they involve related tables and logging is specified in the Controller files;
- Logging contain a
log_namefield that groups log types, and is used to distinguish types of activity and useful to search the History Datatable; - Two special logging are also done:
- Any Dataset download is logged, so administrators may track who and when the dataset was downloaded;
- Any Dataset request is also logged for the same reason
The clean-command of the package SHOULD NOT be used during production, otherwise will just erase all logged changes. If run, will erase the logs older than the time specified in the /config/activitylog.php file.
The ActivityLog table has the following structure:
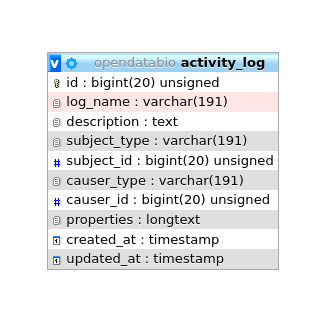
causer_typeandcauser_idwill be the User that made the changesubject_typeandsubject_idwill the model and record changedlog_name- to group logs together and permits queriesdescription- somewhat redundant with log_name in a OpenDataBio context.properties- stores the changes, for example, and identification change will have a log like:
{
"attributes":
{
"person_id":"2",
"taxon_id":"1424",
"modifier":"2",
"biocollection_id":"1",
"biocollection_reference":"1234",
"notes":"A new fake note has been inserted",
"date":"2020-02-08"},
"old":{
"person_id":674,
"taxon_id":1413,
"date":"1995-00-00",
"modifier":0,
"biocollection_id":null,
"notes":null,
"biocollection_reference":null
}
}